
-----
Required Current Density for Electropolishing
Q. Hi, I have a related question about electrochemical polishing. I am currently polishing the inside of a T-tube part. All of them have a very good glossy finish except for the last position of the two sides of the tube, it looks like nicks or pits (photos attached).



I've tried increasing or decreasing the current density, voltage, temperature, fluid flow, all of which create this pitting, which accounts for 80% of polishing output. I have degreased the product with NaOH solution.
Please help me find the cause and prevent pitting on the product.
Thanks very much!
Sorry but, because I don't know much English, I used google.
- Vietnam Hanoi
August 29, 2022
2nd Request Anybody can help me?
Kinh Dinh- Vietnam Hanoi
September 12, 2022
A. Hi Kinh. Sorry that I don't really quite understand the graphics, but is it possible that the cone shape is welded to the tube shape, and that this defect is occurring as electropolishing reveals the weld line? If so, the problem must be resolved with better welding or better welding material.
Luck & Regards,

Ted Mooney, P.E. RET
Striving to live Aloha
finishing.com - Pine Beach, New Jersey
Ted is available for instant help
or longer-term assistance.
![]() Thanks, I found the cause of this problem.
Thanks, I found the cause of this problem.
Thank you so much!
- Vietnam Hanoi
May 12, 2023
⇩ Related postings, oldest first ⇩
Q. We have a business doing Photo Chemical Milling (Acid Etching) and fine laser cutting (down to 20 microns). As part of this, we have an Electropolishing Bath, the solution is made from phosphoric and sulfuric acid. Typically, we electropolish 304 stainless that is about 500 mm x 500 mm (20" x 20") and 0.005" thick. We have mixed success with this, and current is usually 100 - 150 amps. It is adjusted, dependent on the actual size in reference to a chart we were given by the guy that installed the bath. He is no longer around.
I have been trying to find a reliable guide to the required current density. I have the Canning Handbook, which seems to indicate a far higher current density than we are presently using.
Now to the specifics of my current problem:
I need to polish an item with a surface area of 3400 mm2 (5 square inches) and I need to know what current to apply and for how long. I need a very high quality result and cannot afford to damage the items to be polished. Could someone please advise either/both the required and recommended current density and/or the appropriate formula?
Readers may also be interested to note our experience with air agitation of the electropolishing bath...
Our air supply for the factory and laser passes through an air dryer and we almost never get any moisture at the various filter/drain points in the distribution system. Surprisingly though, when we commenced air agitation of the phosphoric/sulfuric mixture, our tank liquid volume has grown by a significant amount - about 10% in 2 months. This can only be from moisture from the air supply! That said, I will be replacing the current mixture with a new solution before attempting to polish the above mentioned item. (This leads to another question - why do some polishing solutions recommend a percentage of water be added to the phosphoric/sulfuric mixture when others specifically advise to keep water out of this solution?)
Metal cutting and finishing - Burleigh, Gold Coast, Australia
August 4, 2010
A. Hi Jim,
Starting with the first question: yes, you seem to have a too low CD for your electropolishing activity. If typically you use 100 - 150 A for a surface area of 50 dm2, you will only have 2 - 3 A/dm2 where an average of 10 A/dm2 would be a much more "normal" value.
Concerning the water coming into your electrolyte: I always learned that the concentrated sulfuric acid has hygroscopic properties and so slowly attracts water from the ambient atmosphere. Maybe your air supply contains water or, by applying air agitation, you increase the contact area between your solution and the outside air, thereby enhancing the influx of moisture.
From theory, the solution works best with as little water in it as possible. If the water concentration becomes too high, instead of polishing, you will get an etching of the surface and in the worst situation, you will even get a grain boundary attack. By increasing the CD, you will come back in an electropolishing current density range, however this has a limit as well and your operation window becomes smaller and smaller.
Why people add water? Maybe to stabilise the concentration and so the working conditions, as inevitably it will contain water after some period of time.
The 3400 mm2 part:
If your 2 - 3 A/dm2 worked always OK in the past, that will give you a nice starting point. In your situation, not knowing if the geometry is complex or not, I would calculate with an average CD of 5A/dm for a complex geometry and if it's only a plain sheet I would go for 10 A/dm2, which will mean a current of 1,7A only for this part of 3400 mm2 in the complex form and 3,4 as plain sheet.
Please make sure that you have a suited rectifier for a job like this, you cannot use your usual one! The reading will be too inaccurate. Use a 5 or 10 A max. rectifier.
The question for the time is a nice one, but unfortunately this is, together with your remark that you need "a high quality result" impossible to answer scientifically. You should know the actual roughness now and have to define the required roughness after electropolishing. If we assume that the electropolishing process will dissolve the surface with the same parameters as for Ni-deposition, you will dissolve 0,205 µ/Aminute/dm2. This will mean that after 10 minutes at this 1,7 A/dm2 you will have a situation that on average 3,5 you is dissolved and that should be more than enough to obtain the optimum result possible for the complex part. Double the CD and use 5' for the simple part. Longer electropolishing will make no sense.
Make sure that you enter the solution with either a dry part or remove excessive water first before entering and then dip the part in the solution turn it around a few time and switch on the rectifier.
So this is what I should do in your place and before the start, I would cross my fingers for a moment too, in order to exclude Murphy and O'Toole (Murphy: What can go wrong, will go wrong, O'Toole: Murphy's law always occurs at the most unwanted moments).
In order to minimise your risk, you could spend some time in additional experimenting with similar base material and investigate for example your current density range. Higher CD's are the standard (Even up to 25 A/dm2).
By the way, I assume that the temperature of your electrolyte is somewhere in the range of 60 - 80 °C? If not, go for the lower current densities you used to apply!
Best regards and Success, always eager to hear if you succeeded with the job.
Harry.

Harry van der Zanden
consultant - Tilburg, Netherlands
Q. Respected sir/ madam
I srinivas Ratod am studying about electropolishing and am confused about the calculation of the voltage and current. Could you please help me how to find the voltage and current of a tube? Specifications are (41.5 OD x 41ID and 152 mm length). Please reply as early as possible.
Thanks and Regards,
Quality Engineer - Bangalore, India
July 8, 2014
A. Hi Srinivas. Harry has offered good advise on current density, saying about 10 A/dm2 (93 A/ft2) is "normal", and up to 25 A/dm2 (230 A/gt2) may be doable. This concurs well with sources such as the Electroplating Handbook, which says 50-500 A/ft2. I would figure 14 A/dm2 (150 A/ft2) is a good number. Voltage is whatever is required to sustain that amperage considering the conductivity of the solution, and will depend on cathode placement and the conductivity of the chosen electropolishing solution, but 6-12 V would be pretty normal.
The electricity will follow the path of least resistance, so there will be little polishing on the ID if you use tank anodes.
Regards,

Ted Mooney, P.E.
Striving to live Aloha
finishing.com - Pine Beach, New Jersey
Ted is available for instant help
or longer-term assistance.
⇦ Tip: Readers want to learn from your situation;
so some readers skip abstract questions.
Q. What are specific electropolishing parameters?
Like volt
Amp
Temperature.
Time
- Satara Maharashtra
March 12, 2021
A. Hi Santosh. Amperage and voltage are discussed reasonably deeply on this page already. Temperature is probably not lower than 45 °C, but 60-80 °C is more typical. Time is completely dependent on how much material you want to remove -- 3 to 4 minutes might be right for metallographic work, 20 minutes is probably more typical for production, and even more time than that is not unusual.
"Specific" answers require specific questions. What are you electropolishing and why please? What problem motivates you to ask? Thanks!
Luck & Regards,

Ted Mooney, P.E. RET
Striving to live Aloha
finishing.com - Pine Beach, New Jersey
Ted is available for instant help
or longer-term assistance.
Q. 'Frosted mark' after EP?
Hello,
After EP, we found some white traces on our workpieces. Our quality control team calls them frosted mark.
At first I thought it must be a contaminant from a previous process, so I noted all the possible contaminants (grease, hydraulic oil from our stamping machine, a water displacing agent) and tested them without success in recreating this defect.
I also tried to reduce the iron concentration in our EP bath but we still have this defect on some of the following batches.
The problem appears randomly but I fear that it will occur more frequently in the future.
For info, our workpieces are small stainless steel wires of around 1 mm in diameter. We work with a 1:1 H3PO4/H2SO4 bath. Our workpieces are pre cleaned with a type of hydrocarbon solvent to remove oil, grease and any organic contaminant prior to EP.
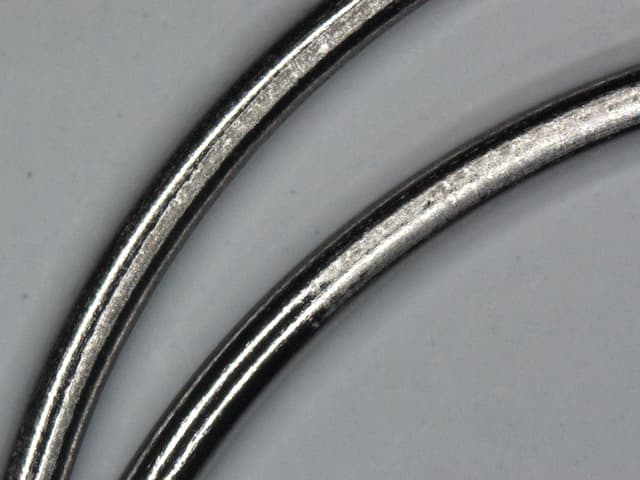
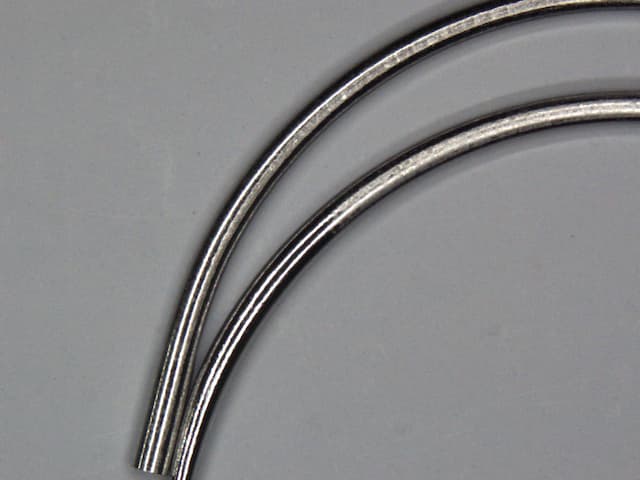


Could you confirm the defect resembles to what we would normally call frosted defect? If so, do you have any more ideas or clues on the possible cause?
Thank you in advance.
- Samut Prakan, Thailand
May 10, 2022
and Chemical Polishing
of Metals in
Research and Industry"
by W.J. Tegart

on eBay or Amazon
or AbeBooks
(affil link)
A. Hi Aimran.
'Etching' is a common defect in electropolishing. Although you say that the problem is random, is it possible that it effects low current density areas rather than high current density ones?
Luck & Regards,

Ted Mooney, P.E. RET
Striving to live Aloha
finishing.com - Pine Beach, New Jersey
Ted is available for instant help
or longer-term assistance.
May 2022
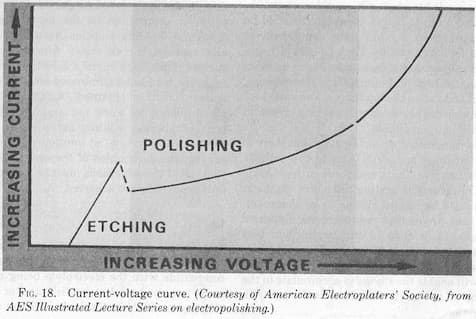
Q. Hello Ted,
Thank you for your input. Effectively, we thought that those areas are where current density is lower. Do you know what could cause this uneven current density? We thought that maybe a residue film stayed on some of the areas, and caused the uneven attack. We are still searching what residue it is, for the moment all our tests to contaminate the part voluntarily have failed.
Anyway, thank you again for your help.
- Samut Prakan, Thailand
June 8, 2022
A. Hi again, Aimran. Per your earlier postings you know that electricity "follows the path of least resistance", so the anode arrangement can affect current distribution. As a general rule, increasing the current density in electropolishing usually doesn't do much harm, whereas reducing it can let you drop into the etching zone. So if experimentation is practical, you might see what happens at higher current density.
A library may have a copy of the Electroplating Engineering Handbook, which has a good chapter on electropolishing.
Luck & Regards,

Ted Mooney, P.E. RET
Striving to live Aloha
finishing.com - Pine Beach, New Jersey
Ted is available for instant help
or longer-term assistance.
Q, A, or Comment on THIS thread -or- Start a NEW Thread

